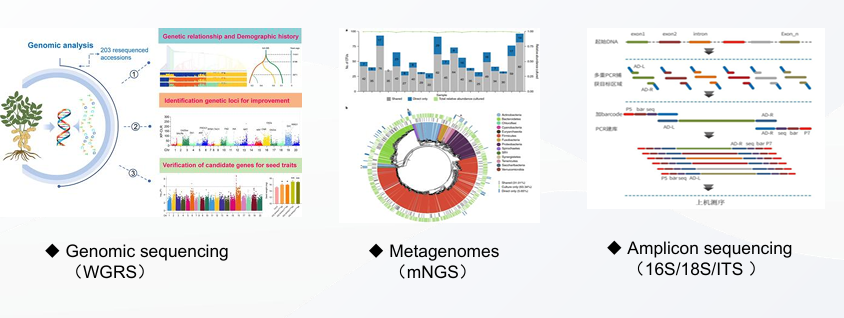
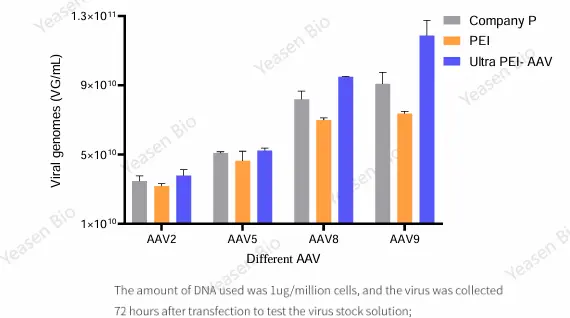
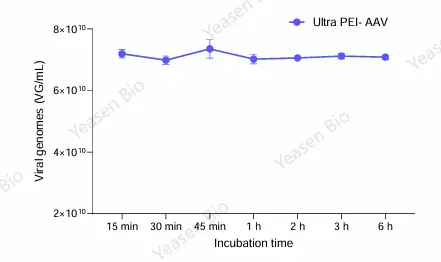
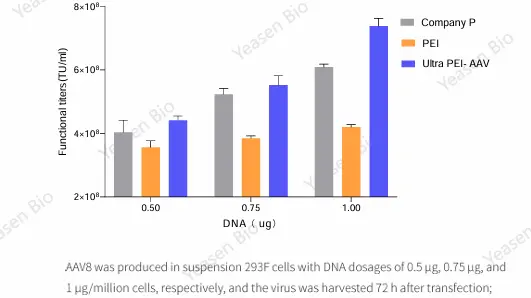
NGS is a high-throughput sequencing method that allows millions or even billions of DNA strands to be sequenced in parallel. Unlike traditional Sanger sequencing, which sequences one DNA fragment at a time, NGS can sequence large genomic regions, entire genomes, or transcriptomes efficiently and affordably.
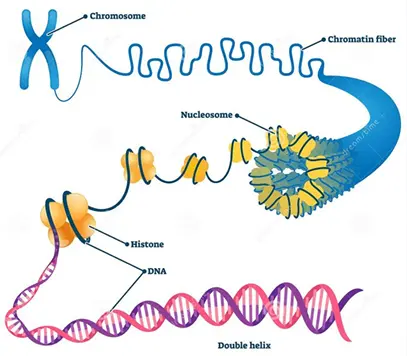
Sequencing: Understanding all the base sequences of a gene or species
The number of chromosomes in each
species is not consistent, and the DNA size
of each chromosome is not consistent. For
example, humans have 23 pairs of
chromosomes, with a total size of about 3 G,
and watermelon has 11 chromosomes, with
a total size of about 365 Mb.
DNA: consists of A, T, C, G four bases
randomly arranged, one base is 1 bp.
1 G=1024 M=1024 * 1024 Kb=1024 * 1024 * 1024 bp.
First Generation sequencing: Sanger sequencing
- First-generation sequencing’s single read length is 800 bp;
- High accuracy, current gold standard for the sequencing;
- Molecular cloning is often performed after first-generation sequencing;
- Only one sequence can be measured at one time.

Use NGS technology to complete scientific research, and publish articles finally
- Customer groups:
- Customers are engaged in Sci-Tech services (NGS technology services, metabolomics services, proteomics services) – Universities, scientific research units, research institutes, and so on who outsource to others.
- Universities, scientific research units, research institutes, and so on who operate by their own.
- Samples: There are various samples (plants, animals, tissues, blood, soil, etc.), and products are required to be universal.
- Automatic database building: large units, with obvious automation requirements, kit script adaptation, would like to try if there is a reduced experimental process and artificial reagents.
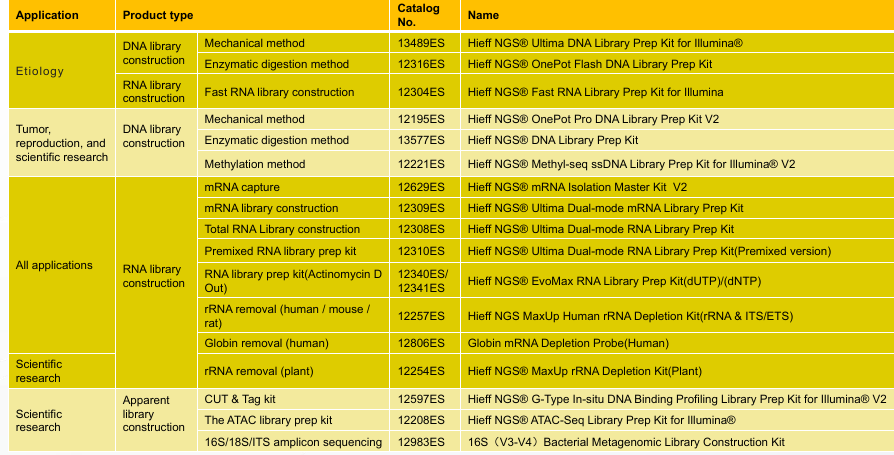
- Product requirements: DNA library construction, RNA library construction, and apparent library construction – kits need to be universal.
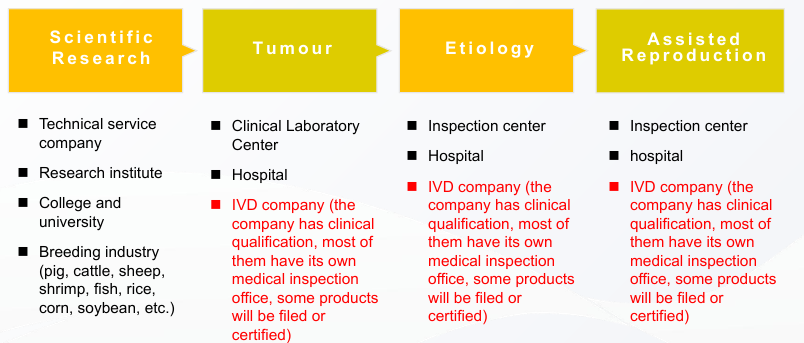
The application in breeding is mainly using NGS technology to assist in variety selection or quality selection
- Customer groups:
- And Breeding Services, Inc.
- The Breeding Industry Corporation (Bayer, et al.).
- Seed industry qualification certification units, livestock and poultry inspection station, etc.
- Sample: single sample type (Customers mainly focus on the pig, cattle, sheep, rice, corn, etc., to establish their own evaluation system).
- Automated library construction: many samples and high degree of automation.
- Product requirements: DNA library construction (main), RNA library construction (less) — success rate.
DNA sequencing
is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides—adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G)—in a DNA molecule. By reading this sequence, scientists can learn about the genetic information contained within DNA, which is essential for understanding gene function, identifying mutations associated with diseases, and advancing fields like personalized medicine, evolutionary biology, and forensic science.